Stages of eye cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the organ have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome (your prognosis).
The most common staging system for eye cancer is the TNM system. For eye cancer there are 4 stages. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the larger the cancer is or the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
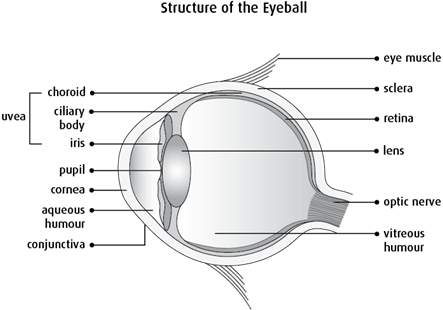
When describing the stage, doctors may use the words intraocular, extraocular, regional or distant. Intraocular means that the cancer is only inside the eye. Extraocular means that the cancer has grown outside of the eye. Regional means close to or around the eye. Distant means in a part of the body farther from the eye.
Find out more about staging cancer.
Stages of intraocular melanoma of the iris
Stage of intraocular melanoma of the iris is based on the size of the tumour, where the tumour is in the eye and if it has spread outside of the eye.
Stage 1
The tumour is only in the iris and is not more than 1/4 the size of the iris.
Stage 2A
The tumour is any of the following:
- It is only in the iris and is more than 1/4 the size of the iris.
- It is only in the iris and is causing glaucoma.
- It has grown next to or into the ciliary body without causing glaucoma.
Stage 2B
The tumour has grown next to or into the choroid without causing glaucoma.
Or
The tumour has grown next to or into the ciliary body, choroid or both. The tumour has also grown into the sclera.
Stage 3A
The tumour has grown next to or into the ciliary body, choroid or both and is causing glaucoma.
Or
The tumour has grown outside of the sclera and this part of the tumour is not larger than 5 mm in diameter.
Stage 3B
The tumour has grown outside of the sclera and this part of the tumour is more than 5 mm in diameter.
Stage 4
The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (called distant metastasis), such as to the lungs, liver or bone. Cancer that has spread to a distant part of the body is also called metastatic eye cancer.
Stages of intraocular melanoma of the ciliary body and choroid
Stage of intraocular melanoma of the ciliary body and choroid is based on the size of the tumour, where the tumour is in the eye and if it has grown outside of the eye or spread to other parts of the body.
Size category
A size category is given from 1 to 4 for melanoma of the ciliary body and choroid. The size category is based on the thickness (height) and largest diameter at the base of the tumour. Category 1 tumours are the smallest and category 4 tumours are the largest.
Category 1
The tumour is either:
- not more than 12 mm wide and not more than 3 mm thick
- not more than 9 mm wide and 3.1 to 6 mm thick
Category 2
The tumour is any of the following:
- 12.1 to 18 mm wide and not more than 3 mm thick
- 9.1 to 15 mm wide and 3.1 to 6 mm thick
- not more than 12 mm wide and 6.1 to 9 mm thick
Category 3
The tumour is one of the following:
- 15.1 to 18 mm wide and 3.1 to 6 mm thick
- 12.1 to 18 mm wide and 6.1 to 9 mm thick
- 3.1 to 18 mm wide and 9.1 to 12 mm thick
- 9.1 to 15 mm wide and 12.1 to 15 mm thick
Category 4
The tumour is one of the following:
- more than 18 mm wide and may be any thickness
- 15.1 to 18 mm wide and 12.1 to 15 mm thick
- 12.1 to 18 mm wide and more than 15 mm thick
Stage 1
The tumour is size category 1 and only in the choroid.
Stage 2A
The tumour is size category 1 and one of the following:
- The tumour has grown into the ciliary body.
- The tumour has grown outside the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
- The tumour has grown into the ciliary body and outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour outside of the eyeball is not more than 5 mm thick.
- The tumour is size category 2 and is only in the choroid.
Stage 2B
The tumour is size category 2 and has grown into the ciliary body.
Or
The tumour is size category 3 and only in the choroid.
Stage 3A
The tumour is one of the following:
- It is size category 2 and has grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour outside of the eyeball is not more than 5 mm thick.
- It is size category 2 and has grown into the ciliary body. The tumour has also grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
- It is size category 3 and has grown into the ciliary body.
- It is size category 3. It has grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
- It is size category 4 and only in the choroid.
Stage 3B
The tumour is one of the following:
- It is size category 3 and has grown into the ciliary body. The tumour has also grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
- It is size category 4 and has grown into the ciliary body.
- It is size category 4. It has grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
Stage 3C
The tumour is size category 4 and has grown into the ciliary body. It has also grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is not more than 5 mm thick.
Or
The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball, and this part of the tumour is more than 5 mm thick.
Stage 4
The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body (called distant metastasis), such as to the lungs, liver or bone. Cancer that has spread to a distant part of the body is also called metastatic eye cancer.
Recurrent eye cancer
Recurrent eye cancer means that the cancer has come back after it has been treated. If it comes back in the same place that the cancer first started, it’s called local recurrence. If it comes back in tissues or lymph nodes close to where it first started, it’s called regional recurrence. It can also recur in another part of the body. This is called distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
