The blood and bone marrow
The blood is made up of blood cells in a liquid called plasma. Blood cells are made in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy area inside most bones.
Blood
Blood is a mixture of plasma and blood cells. Plasma is mostly water but also has protein, salts, fats and sugar (glucose). Blood carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste products, cells and hormones. It is part of the circulatory system that includes the heart and blood vessels. Testing the blood is an easy way for doctors to look for signs of disease and manage treatment for disease.
Types of blood cells
There are 3 types of blood cells – red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) carry oxygen to all cells in the body. The oxygen is carried to cells on a protein in red blood cells (called hemoglobin). Hemoglobin is what makes the blood red. It also carries carbon dioxide away from cells so that it can be exhaled by the lungs. Almost all of the cells in the blood are red blood cells.
White blood cells (leukocytes) are an important part of the
Platelets (thrombocytes) make the blood clot and help stop bleeding. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets travel to the area and clump together.
Types of white blood cells
There are different types of white blood cells. Each type has a different job.
Lymphocytes make antibodies to fight infection. They are found in the lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, tonsils, adenoids and bone marrow. They are also found in lymphatic tissue in other parts of the body, such as the appendix, the small intestine and other parts of the digestive system and respiratory system.
The 3 main types of lymphocytes are:
- B cells, which make antibodies to fight bacteria, viruses and other foreign material, such as fungi
- T cells, which fight infection, destroy abnormal cells and control the immune response
- natural killer (NK) cells, which attack any foreign cells
Granulocytes fight infection and become active in response to tissue inflammation. The 3 main types of granulocytes are:
- neutrophils, which fight infection by surrounding and eating (ingesting) bacteria
- eosinophils and basophils, which attack and destroy certain parasites and are activated during an allergic reaction
Monocytes help fight infection by changing into cells called macrophages, which eat foreign invaders, such as bacteria and waste from dying cells.
How blood cells are formed
Blood cells are formed through a process called hematopoiesis. All blood cells develop from young, immature cells called stem cells. Stem cells can change into the different types of cells, depending on what the body needs. Stem cells develop and mature into the various types of cells by a process called differentiation.
Stem cells
Stem cells are found in the bone marrow, blood and umbilical cord blood. Stem cells develop into blood cells in the bone marrow. When blood cells are mature and able to function, they leave the bone marrow and move into the blood.
In adults, most stem cells are found in the bone marrow. Stem cells can also be found in smaller amounts in the bloodstream. These are called peripheral blood stem cells. Umbilical cord blood also has stem cells but there are fewer stem cells than those in the bone marrow and blood.
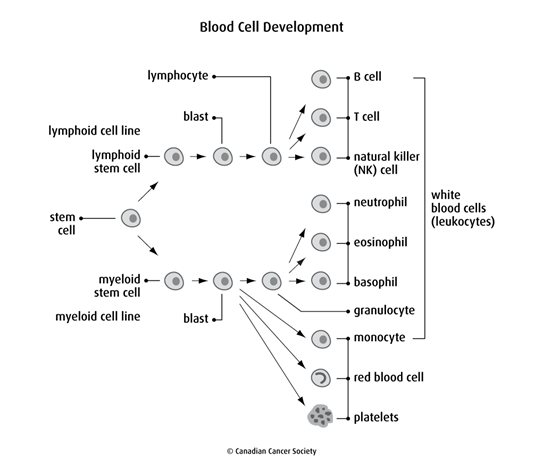
Blood cell development
In the earliest stage of blood cell development, stem cells begin to develop into either the lymphoid cell line or the myeloid cell line. In both cell lines, the stem cells become blasts, which are still immature cells.
Lymphoid cell line
Lymphoid stem cells develop into lymphoblasts, which develop into lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. Lymphocytes help fight infection and destroy abnormal cells.
Myeloid cell line
Myeloid stem cells develop into red blood cells, platelets and other types of white blood cells (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils and monocytes). Red blood cells carry oxygen to all tissues of the body. Platelets form clots in damaged blood vessels to stop bleeding.
Myeloid progenitor cells develop into 2 different types of white blood cells – granulocytes and monocytes. These white blood cells destroy bacteria and other foreign invaders and help fight infection.
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy area inside most bones. It makes blood cells.
There are 2 main types of bone marrow – red and yellow. Red bone marrow is where stem cells develop into red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Yellow bone marrow stores fatty tissue.
In adults, the bone marrow that makes the most blood cells is found in the hip bones (bones of the
